- Type:
- Industry News
- Date
- 2025-Dec-23
Double-Ended Markers: From Production to Core Technology
Double-ended markers have become common tools in art, design, education, and office environments. Their ability to combine two tips with different functions into a single marker offers both convenience and versatility. To understand their value, it is useful to examine how these markers are produced and what technologies support their reliable performance.
.jpg)
What Is the Production Process of Double-Ended Markers?
The production of double-ended markers follows a carefully controlled sequence to ensure consistent ink flow, durability, and user comfort. Each step contributes to the final performance of the marker.
• Product design and specification
- Define marker length, diameter, and balance
- Select tip types, such as fine, brush, chisel, or broad
- Determine ink capacity and color range
• Ink formulation
- Develop ink based on intended use (water-based, alcohol-based, or hybrid)
- Test for color consistency, drying time, and flow stability
- Adjust viscosity to support two tips sharing one ink reservoir
• Tip manufacturing
- Produce fiber or felt tips with controlled density
- Cut and shape tips according to line-width requirements
- Test resilience to pressure and repeated use
• Barrel and internal component production
- Mold marker barrels using plastic materials for strength and lightness
- Manufacture internal reservoirs and connectors to regulate ink delivery
- Ensure airtight seals to reduce ink evaporation
• Assembly process
- Insert ink reservoir into the barrel
- Attach tips securely at both ends
- Add caps with proper sealing mechanisms
• Quality inspection and testing
- Check ink flow from both ends
- Test writing smoothness and color accuracy
- Inspect for leakage, imbalance, or air gaps
• Packaging and distribution
- Label markers by color and tip type
- Package individually or in sets
- Prepare for storage and transport under controlled conditions
This structured production process ensures that double-ended markers meet performance expectations while remaining practical for daily use.
.jpg)
The Technology Behind Double-Sided Markers
Ink Distribution and Flow Control
One of the important technologies behind double-sided markers is ink distribution. Unlike single-tip markers, double-ended markers must deliver ink evenly to two separate tips from a shared reservoir. Internal fiber cores or sponge-based reservoirs are designed to regulate ink movement through capillary action. This system ensures that both tips receive a consistent supply without one end drying out faster than the other. Engineers carefully balance ink absorption and release rates to maintain uniform performance over time.
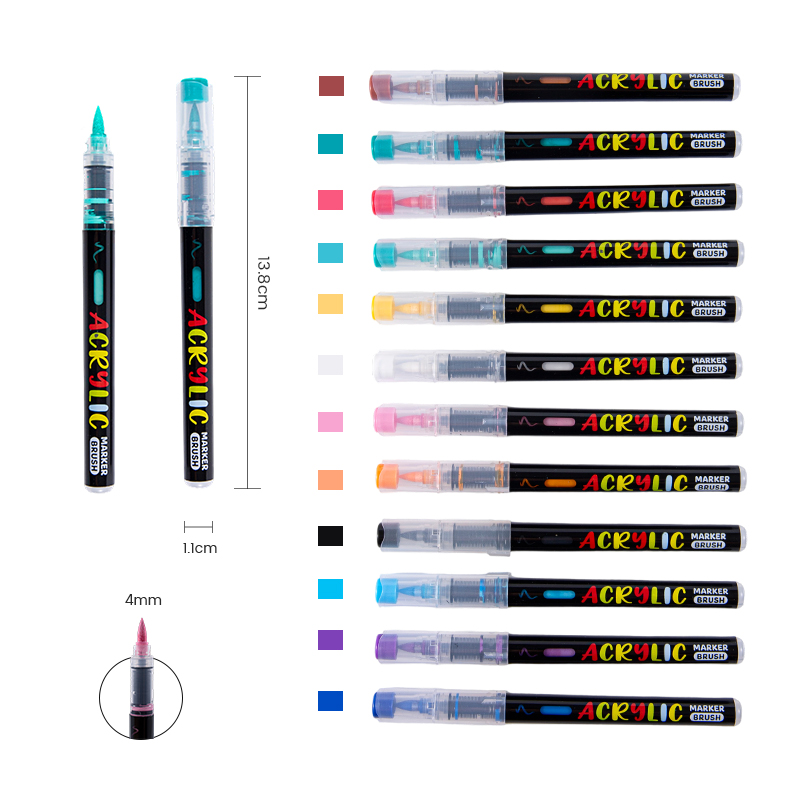
Tip Engineering and Material Science
The tips of double-sided markers are the primary contact point between ink and surface, making their design critical. Different tip shapes require different fiber densities and structural strength. For example, a brush tip must be flexible yet durable, while a fine tip requires precision and resistance to fraying. Advances in material science allow manufacturers to produce tips that maintain shape even under repeated pressure. These developments support cleaner lines, predictable ink flow, and longer usable life.
Sealing, Durability, and User Safety
Another key technological area involves sealing and durability. Double-ended markers require caps on both ends, each designed to prevent air from entering the barrel. Airtight sealing reduces ink evaporation and extends shelf life. At the same time, cap design often includes features such as clip integration or ventilation holes to support safety standards. Barrel materials are selected to resist cracking and deformation, ensuring the marker remains reliable even with frequent handling.
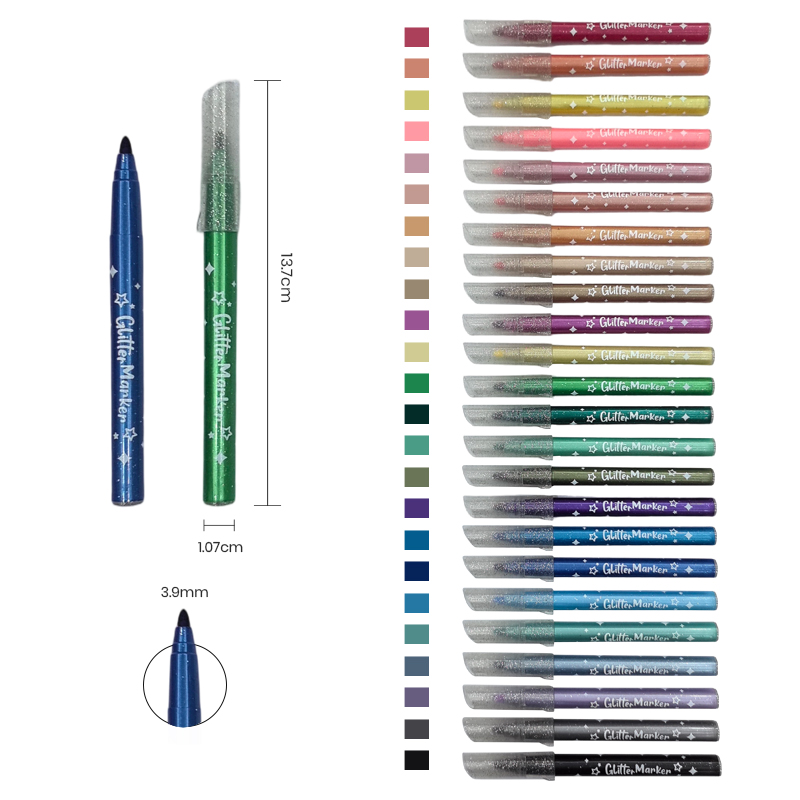
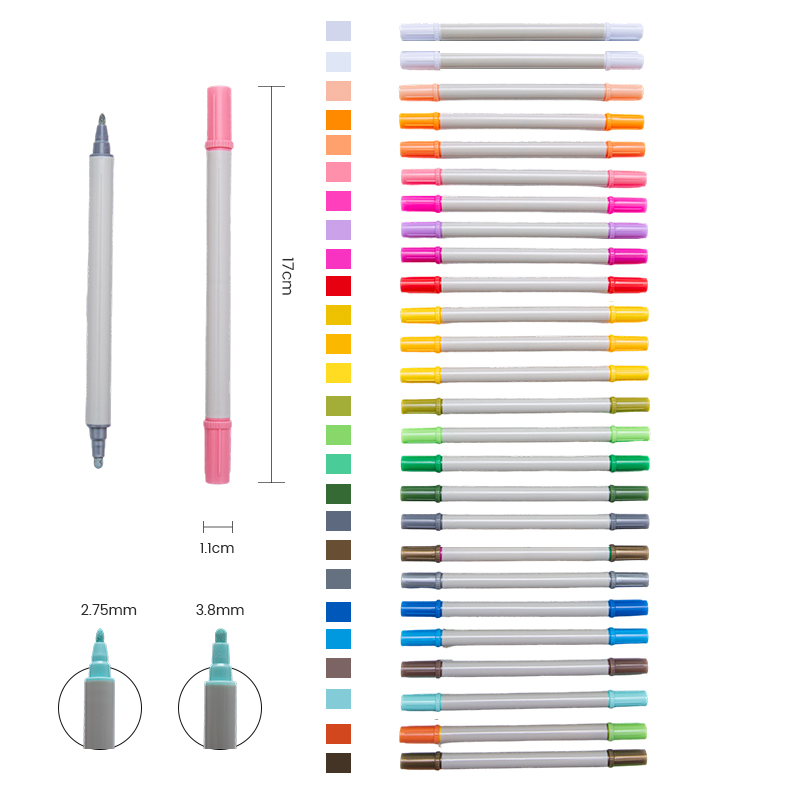
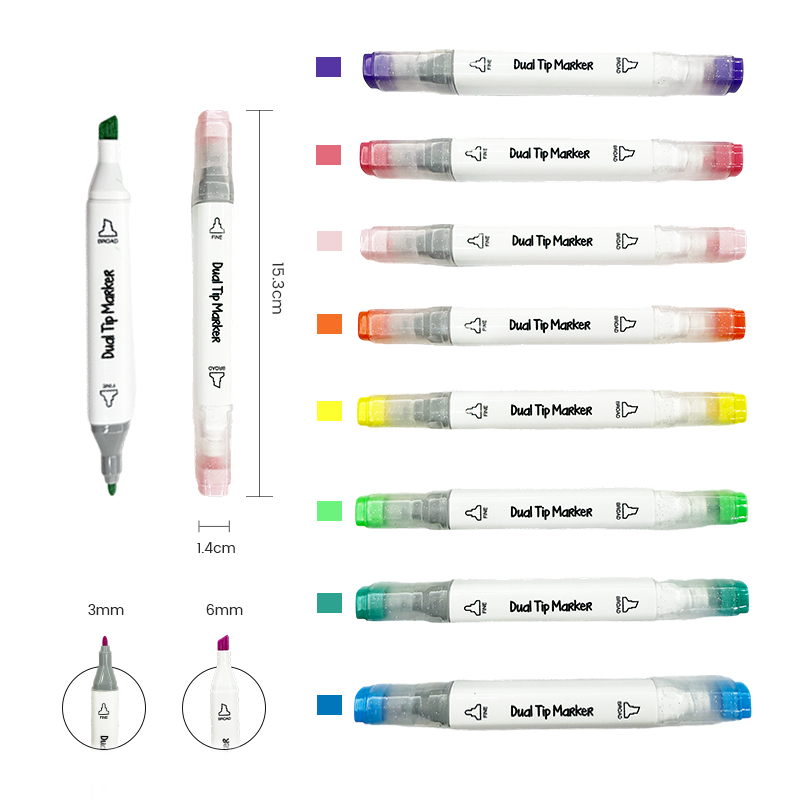
Characteristics of Twin-Tip Markers and Highlighters
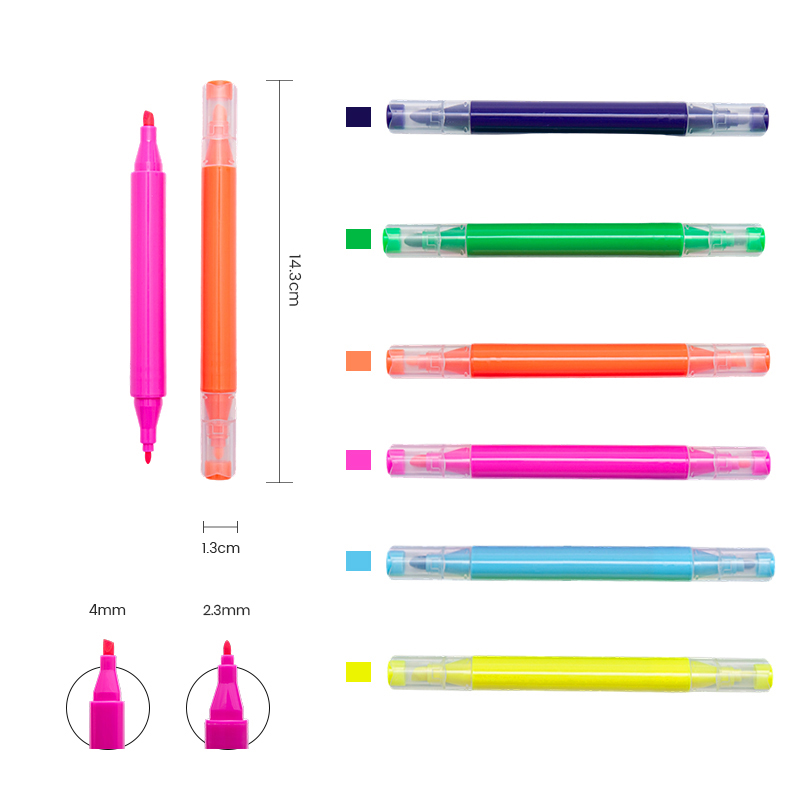

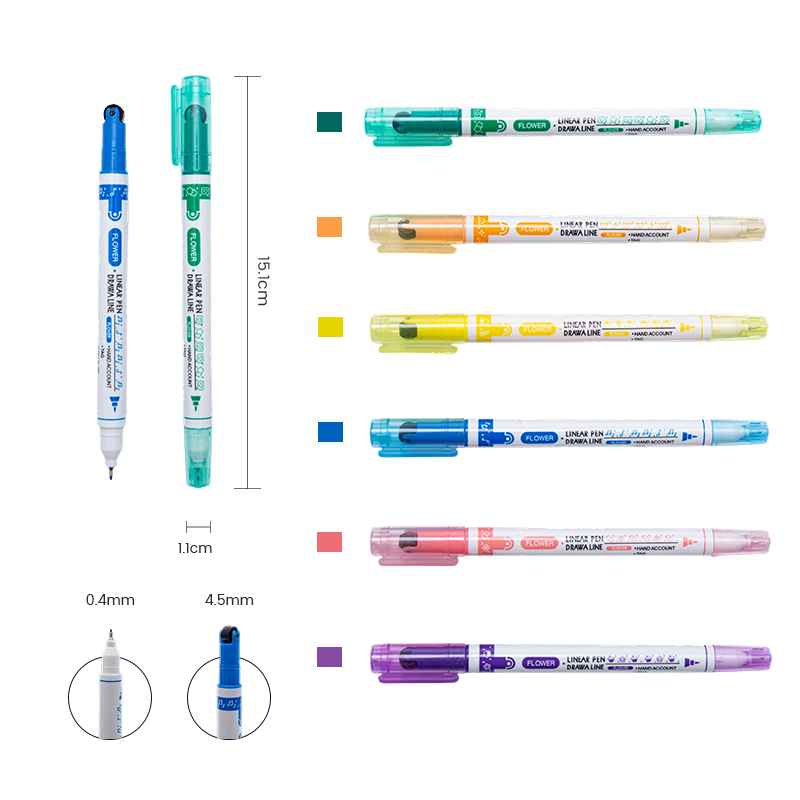
Twin-tip markers typically feature a fine tip on one end and a broader tip or brush on the other. This dual functionality provides flexibility in both detailed and expansive work. Fine tips are ideal for precise writing, technical sketches, outlining, or intricate patterns. Broader tips, in contrast, are used for coloring, highlighting, or filling larger areas quickly.
Highlighters, when designed with twin tips, combine a standard chisel tip with a finer end for precision marking. The chisel tip covers larger text sections effectively, while the fine tip enables underlining or annotation without obscuring important details. The ink in twin-tip markers and highlighters is often water-based or alcohol-based, providing smooth flow, vibrant color, and minimal bleeding. Many are also designed to be smudge-resistant and fast-drying, which enhances usability in everyday tasks.
Portability is another notable characteristic. The twin-tip design reduces the need for multiple pens or highlighters, allowing users to carry a single versatile tool. Ergonomic barrel shapes and comfortable grips further improve usability, especially for prolonged writing or highlighting sessions.
Uses and Applications
The versatility of twin-tip markers and highlighters allows them to be used in a variety of settings, including classrooms, offices, art studios, and personal projects. They are particularly effective in environments where alternating between detailed work and broader marking is required. Below is a table illustrating the main characteristics and uses of twin-tip markers and highlighters:
|
Tool Type |
Characteristics |
Primary Uses |
Ideal Users |
|
Twin-Tip Marker |
Fine tip + broad tip, water/alcohol-based ink, vibrant colors |
Outlining, sketching, calligraphy, coloring |
Artists, students, designers |
|
Twin-Tip Highlighter |
Chisel tip + fine tip, translucent ink, quick-drying |
Highlighting text, underlining, note-taking |
Office workers, students, researchers |
|
Both |
Dual-function tips in one pen, portable, ergonomic |
Switching between detailed and broad strokes without changing tools |
Professionals, hobbyists, educators |
For example, students can use twin-tip markers for both annotating text and creating colorful diagrams in notes. In professional settings, office workers can highlight key points with the chisel tip and add annotations with the fine tip. Artists often benefit from the ability to switch seamlessly between precision detailing and larger color applications without needing additional tools.
Advantages of Twin-Tip Design
The twin-tip design provides several practical benefits. It enhances efficiency by reducing the need to carry multiple instruments. Users can alternate between tasks without pausing to switch pens or highlighters. Second, it supports creativity and precision simultaneously. Whether drawing intricate patterns, designing layouts, or marking documents, the ability to change tip size ensures both accuracy and speed.
Another advantage is organization. Twin-tip markers and highlighters reduce clutter by consolidating functions into a single tool. This is particularly useful in classrooms, offices, and workspaces with limited storage. Additionally, the consistency of color across both tips allows for smoother transitions in artistic projects or clearer annotations in textual work.
Many twin-tip markers and highlighters are designed for durability. Ink flow is balanced to prevent one tip from running out faster than the other, and tip materials are reinforced to maintain shape during extended use. This ensures that the marker or highlighter provides reliable performance throughout its lifespan.


 English
English
 English
English русский
русский Español
Español